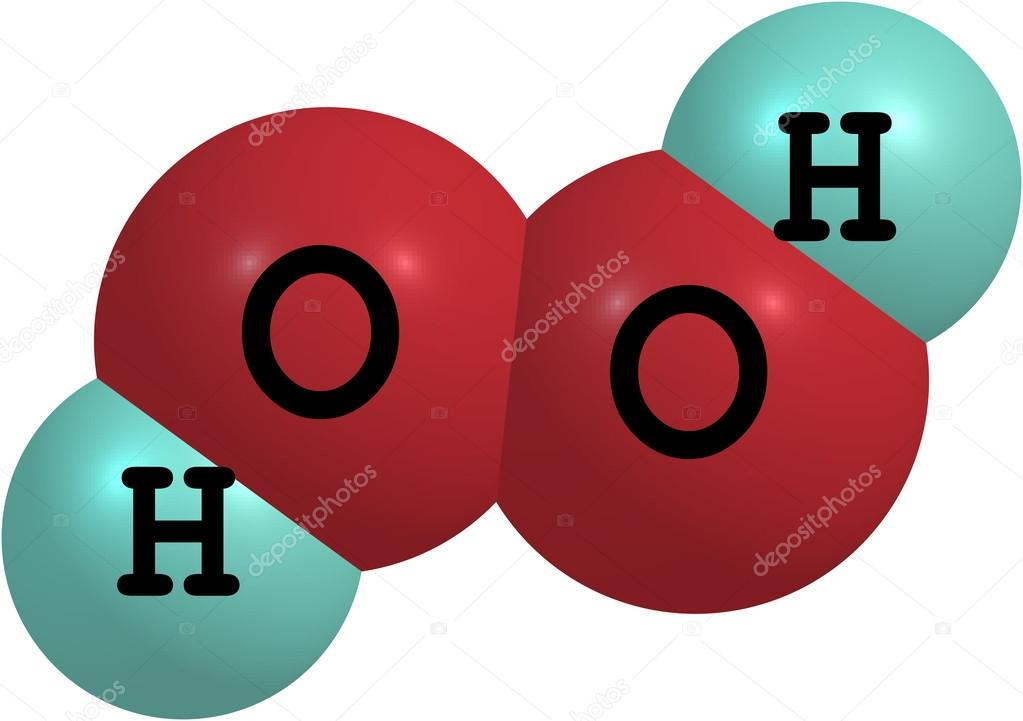
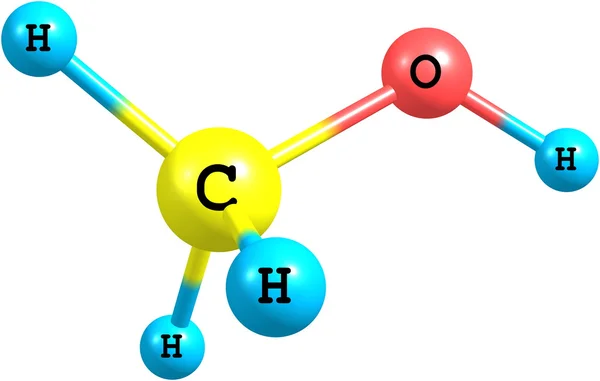
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) molecular structure isolated on white — Photo
L
2000 × 1410JPG6.67 × 4.70" • 300 dpiStandard License
XL
6854 × 4831JPG22.85 × 16.10" • 300 dpiStandard License
super
13708 × 9662JPG45.69 × 32.21" • 300 dpiStandard License
EL
6854 × 4831JPG22.85 × 16.10" • 300 dpiExtended License
Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizer. It is a colorless liquid, slightly more viscous than water
— Photo by olla.davies- Authorolla.davies

- 41912847
- Find Similar Images
- 4.6
Stock Image Keywords:
Same Series:






Similar Stock Videos:


















Usage Information
You can use this royalty-free photo "Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) molecular structure isolated on white" for personal and commercial purposes according to the Standard or Extended License. The Standard License covers most use cases, including advertising, UI designs, and product packaging, and allows up to 500,000 print copies. The Extended License permits all use cases under the Standard License with unlimited print rights and allows you to use the downloaded stock images for merchandise, product resale, or free distribution.
You can buy this stock photo and download it in high resolution up to 6854x4831. Upload Date: Mar 3, 2014